
The world is changing fast, and it's shaking up how we think about education. The old-school model is getting a run for its money from skills-based learning. Did you know that 87% of employers say skills matter more than degrees when hiring? That's a big deal, showing how we're moving from just knowing stuff to being able to do stuff. But what is skills-based learning really about, and how do we make it work for today's jobs? This article will look at ways to make skills-based learning happen, like tying learning to real-world needs, using the latest tech, and encouraging teamwork. Whether you're teaching, making policies, or just love learning, getting these strategies can help you succeed in a world where skills rule. Let's dive into how skills-based learning can make a difference!
Summary: This article describes skills-based learning, focusing on aligning objectives with goals, designing and implementing practical programs, and assessing outcomes, while leveraging technology and addressing psychological aspects. It also covers stakeholder collaboration, overcoming challenges, and includes a FAQ section.
Skills-Based Learning: Understanding the Approach
Definition and Importance of Skills-Based Learning
Skills-based learning is an educational approach that emphasizes the acquisition of specific skills that are directly applicable to real-world scenarios. This method focuses on practical application rather than theoretical knowledge, aiming to equip learners with the tools they need to succeed in their personal and professional lives.
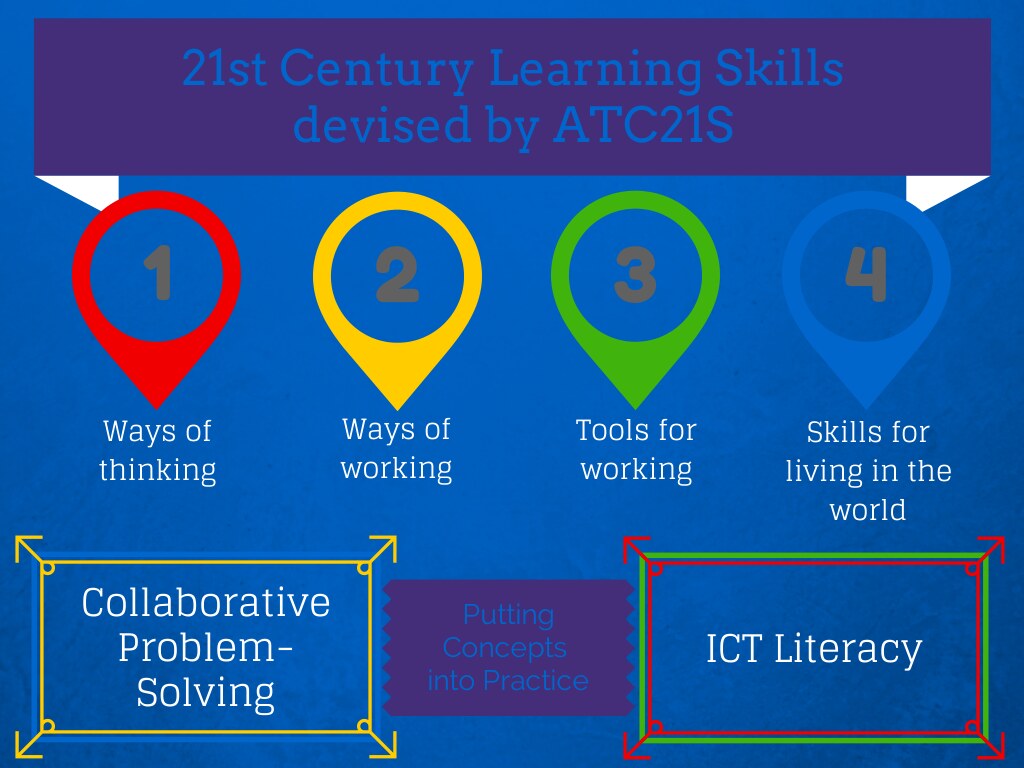
By concentrating on developing competencies such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and effective communication, skills-based learning prepares students to navigate the complexities of modern life and the workforce. This approach is increasingly recognized as essential in an ever-evolving job market, where employers seek individuals who can adapt and apply their skills to various challenges.
Aligning Learning Objectives with Skills-Based Learning Goals
Identifying Skill Gaps for Effective Skills-Based Learning
To ensure that learning goals align with organizational objectives, it is essential to clearly identify skill gaps and needs. This involves aligning assessments with desired learning outcomes. When these elements are not in harmony, it can lead to confusion and difficulty in pinpointing where skills are lacking.
Break down course goals into specific learning objectives to accurately determine the skills required. For example, instead of a broad goal like "understand research methods," specify that students should "analyze features and limitations of various sampling procedures and research methodologies." This specificity ensures that assessments truly reflect the skills you aim to develop.
Clear, specific objectives are crucial for identifying the necessary skills and knowledge, paving the way for effective skills-based learning.
Competency Mapping for Skills-Based Learning Success
Competency mapping is vital for ensuring that learning objectives align with organizational goals. It involves aligning course content, teaching activities, and assessments with clear learning objectives for consistency and impact.
Utilize action verbs in objectives to connect assessments and teaching content to the desired skills. A structured approach to competency mapping includes setting course goals, translating them into learning objectives, and ensuring alignment across all elements.

For instance, a competency map might indicate that for "skills-based learning," students need to employ specific analytical techniques. This is supported by corresponding teaching materials and verified through targeted assignments. Tools like an alignment matrix can be used to map objectives to activities and assessments, creating a cohesive learning experience centered on the right skills.
Designing Skills-Based Learning Programs
Skills-Centered Curriculum Design
Skills-based education focuses on building practical skills and competencies that are key for job performance, rather than just academic knowledge. It uses experiential learning like internships, apprenticeships, projects, and hands-on training to prepare learners for real-world tasks.
By centering curricula on skills, students become more employable, as they're prepared to meet employer expectations right from the start. Additionally, these programs help students adapt and continue learning throughout life, enabling them to update their skills as technology and industry demands evolve.
This approach also boosts confidence and self-efficacy, which can be advantageous in job interviews and when handling workplace challenges. Skill-based learning encourages entrepreneurship and innovation by equipping students with problem-solving skills and an entrepreneurial mindset.

For example, a digital marketing program might integrate theory with practical projects, internships, and real-world client work to build both knowledge and applicable skills.
Customizing Skills-Based Education for Learners
Skills-based education is flexible, allowing curricula to be tailored to fit the needs and career goals of different learners. This customization can involve adjusting the mix of technical and soft skills based on a learner's profile and their target industry.
Programs can be designed to match individual learning speeds and styles through modular, competency-based progressions. This approach helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and the practical skills employers seek, making graduates more job-ready.

Flexible curriculum design also supports ongoing skill development, which is essential for long careers in fast-changing industries. Consider an IT skills program—it might offer beginner, intermediate, and advanced tracks with personalized mentorship and project options based on a learner's background and career goals.
For further reading, explore these resources:
- Skills-based education
- Experiential learning methods
- Entrepreneurship and innovation
- Customizing learning pathways
Implementing Practical Learning Methods for Skills-Based Learning
Project-Based and Scenario-Based Learning Approaches
Project-Based Learning allows students to choose their own topics and set personal goals. This approach enhances:
- Self-motivation
- Critical thinking
- Communication
- Teamwork
By linking theory with real-world applications, students acquire skills that are both durable and adaptable. For instance, in sociology, students might apply theoretical concepts to community service projects. This not only provides practical experience but also deepens their understanding of social theories.

Scenario-Based Learning, in contrast, immerses students in realistic narratives or situations. Here, they must apply their knowledge to solve problems, significantly enhancing their problem-solving and critical thinking skills as they work through solutions.
Hands-On Experience and Simulations in Skills-Based Learning
Hands-On Learning is crucial for reinforcing theoretical concepts and improving problem-solving skills through real-world applications. This method emphasizes active participation, fostering:
- Deep thinking
- A comprehensive understanding of the subject
Kinesthetic Learning involves activities such as drawing, acting, and building, which keep students engaged and help develop skills like hand-eye coordination and analytical thinking.
Simulations and Lab Experiments are indispensable, allowing students to observe, apply, and reflect on concepts, thereby effectively bridging the gap between theory and practice. For example, in chemistry labs, students perform titration experiments to witness chemical reactions firsthand, reinforcing their theoretical knowledge.

Practical-based learning shifts education from rote memorization to active engagement with real-world scenarios. It cultivates critical thinking, creativity, teamwork, and adaptability—skills that are highly valued in the workforce. Explore more on practical-based learning.
Evaluating Skills-Based Learning Outcomes
Effective Strategies for Skills-Based Assessment
Traditional assessments, such as multiple-choice tests, often fall short in reflecting real-world skills. To address this gap, competency-based assessments have emerged as a more effective alternative. These assessments prioritize the demonstration of practical skills over theoretical knowledge by setting clear, skill-oriented goals.

A diverse mix of assessment methods—traditional, formative, competency-based, and portfolio-based—provides a comprehensive view of a student's capabilities. For instance, in nursing programs, students may be required to demonstrate patient care through hands-on simulations or video tasks.
Competency-based education emphasizes assessments that replicate real-world scenarios, leveraging technology and interactive elements like game-based simulations. With advancements in AI, it's now possible to develop scalable, interactive assessments that enable students to collaboratively solve problems on digital platforms.
Continuous Feedback for Skills Mastery
To enhance skills-based learning, a continuous cycle of practice, reflection, assessment, and feedback is essential. Ongoing feedback plays a critical role in helping students monitor their progress and identify areas for improvement. Competency-based learning supports multiple attempts, allowing students to refine their skills until mastery is achieved, making learning a more personalized experience.

The exchange of feedback between students and educators fosters engagement and empowers students to take ownership of their learning journey. For example, business students might lead a team project and receive feedback from both peers and instructors, refining their leadership and teamwork skills through several assessment iterations.
Leveraging Technology in Skills-Based Learning
Technology and AI in Skills-Based Learning
Technology and AI play a significant role in enhancing skills-based learning. These innovations create training environments that prioritize real-world tasks over theoretical knowledge, enabling learners to acquire practical skills. AI tools, such as those offered by Coursera, personalize the learning experience by identifying individual areas for improvement. This personalization makes the learning process more engaging and effective.
By leveraging AI, individuals can continuously develop new skills through flexible online courses and rapid learning modules that align with industry requirements. Furthermore, AI-driven hiring practices enable companies to prioritize skills, broadening their talent pool and enhancing workforce quality. Skills-based organizations utilize technology to assign tasks according to employees' strengths, thereby increasing agility and productivity.
Monitoring Progress in Skills-Based Learning
Monitoring progress in skills-based learning is crucial to ensure its effectiveness. Technology facilitates real-time data and performance assessments, providing immediate feedback and allowing for necessary adjustments. Companies employ skills-based platforms to connect training with job performance, ensuring that acquired skills translate into workplace success.
Skill assessments and certifications enhance job prospects and career advancement. Continuous monitoring is essential for lifelong learning, especially as technology continues to evolve. Data insights empower companies to refine training programs to meet industry demands and career trajectories. Tools like Learning Management Systems (LMS) and talent management software offer skills gap analysis and skills mapping, highlighting skill levels to support ongoing learning and career progression.
Effective Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement in Skills-Based Learning
Building Educator and Industry Partnerships
To make skills-based learning effective, educators and industry must collaborate closely. A stakeholder engagement plan is instrumental in identifying who should be involved and how. This plan ensures that education aligns with workforce needs by fostering open dialogues tailored to stakeholder preferences.

Involving stakeholders early fosters a sense of ownership, increasing their support. This collaboration enables educators and industry to co-create impactful learning programs. Genuine partnerships transcend mere information sharing—they empower stakeholders to contribute to value creation. For example, consider a university partnering with local businesses. Together, they design courses that impart the skills businesses require, utilizing feedback sessions and joint committees to steer decisions.
Employers' Influence in Skills-Based Learning
Employers are pivotal in shaping skills-based learning. They must engage early and frequently with educational institutions to communicate the necessary skills. Tools like stakeholder mapping assist in identifying suitable education partners and determining collaboration strategies.

Such collaboration builds trust and allows employers to influence curricula, ensuring alignment with job market demands. When employers are involved in decision-making, programs become more relevant and widely adopted. For instance, a tech company might collaborate with a community college, offering internships and contributing to course content development. This approach ensures students acquire the in-demand tech skills, preparing them effectively for the workforce.
Overcoming Challenges in Skills-Based Learning
Overcoming Barriers in Skills-Based Learning
Skills-based learning can encounter several challenges, such as the disparity between academic knowledge and job requirements. To bridge this gap, it's effective to combine classroom learning with real-world practice, as exemplified by companies like 21K School.
Hands-on Experience: Engaging in practical experiences not only boosts confidence but also enhances performance in job interviews and workplace tasks.
Continuous Learning: With the rapid pace of technological advancements, continuous learning is crucial. Skills-based education supports adaptability, helping individuals remain agile in evolving environments. More insights can be found at 21K School.
Resistance to Change: Some individuals may resist shifting from traditional methods. However, adopting a flexible, skills-focused approach fosters cross-functional teamwork, as discussed by Gloat.
Skills-Based Hiring Practices: By prioritizing skills over degrees, organizations can access a broader and more qualified candidate pool, a strategy recommended by Coursera.

Psychological and Motivational Benefits of Skills-Based Learning
Boosting Motivation and Confidence through Skills-Based Learning
Skills-based learning significantly boosts motivation and confidence by engaging learners in hands-on activities. This approach not only builds mental resilience but also aids in emotional control by promoting neuroplasticity and strengthening the prefrontal cortex.
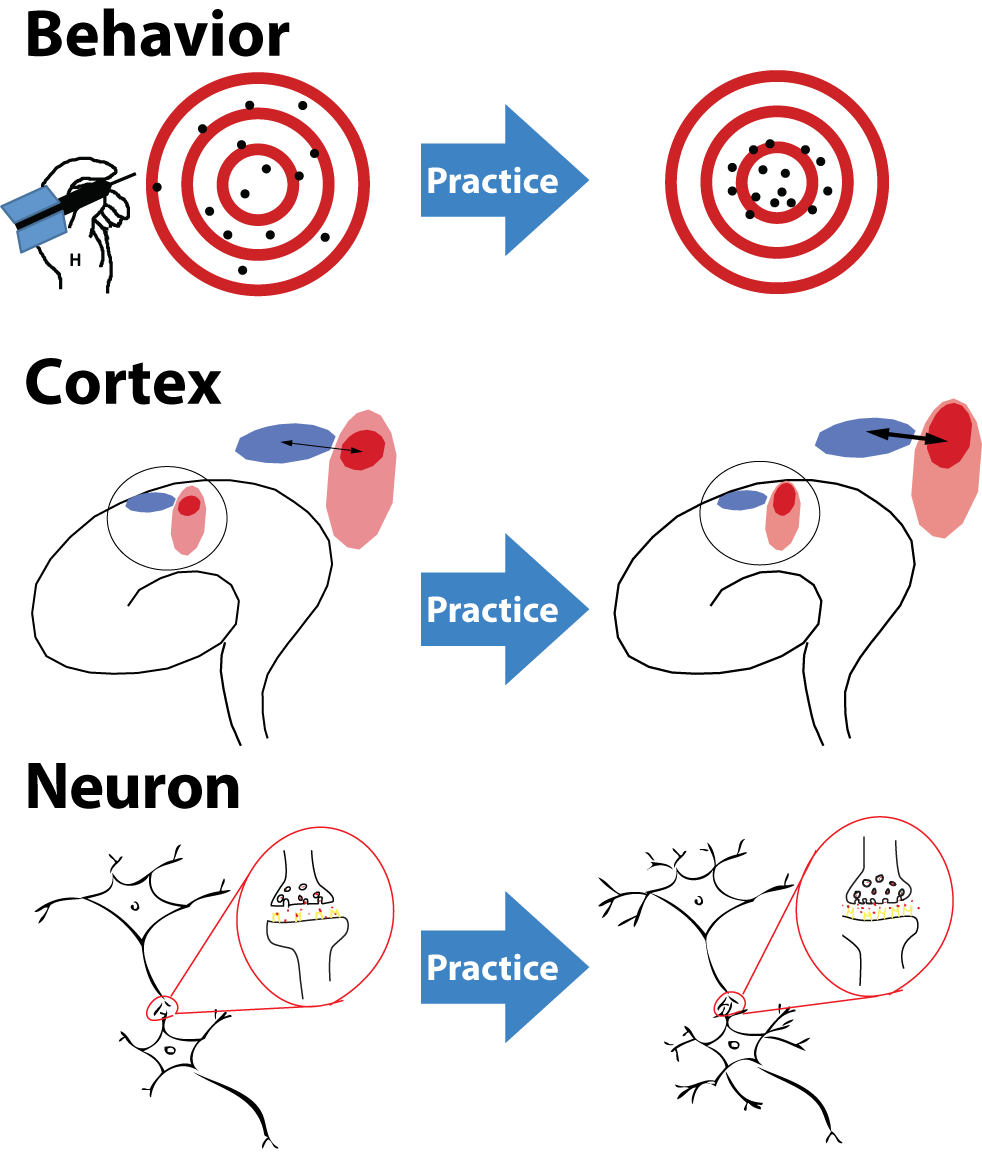
When learners achieve immediate results, such as solving problems or creating tangible items, they experience a sense of accomplishment. This success fuels their desire to continue learning.
Furthermore, project-based learning connects education to real-world scenarios, making it more engaging and fostering a sense of belonging. This method also enhances emotional intelligence by teaching students to manage emotions in group settings, thereby improving communication and conflict resolution skills—essential for both personal and professional life.
Frequently Asked Questions About Skills-Based Learning
Integrating Skills-Based Learning into School Curricula
Schools can effectively integrate skills-based learning by incorporating practical, hands-on tasks into traditional subjects. This approach makes learning more relevant to real life. By including workshops and vocational training alongside theoretical instruction, students gain confidence and become job-ready.
For instance, 21K School advocates for a flexible curriculum that adapts to the evolving demands of work and technology. Schools can also foster an entrepreneurial mindset by encouraging innovation and problem-solving beyond textbooks.
Collaboration across different departments and dismantling traditional barriers can lead to a more dynamic and skills-focused learning environment, as noted by Gloat.
Examples of Successful Skills-Based Learning Programs
Successful skills-based programs align vocational training with industry needs in areas like digital marketing, data analytics, and AI, enhancing students' employability. Programs that blend theory with practical work, such as workshops and internships, help students build confidence and readiness for the workforce.
Schools that introduce entrepreneurial skills early encourage creative thinking and adaptability. Skills-based setups promote cross-functional projects and break down hierarchies, engaging students and enhancing skill acquisition. According to the India Skills Report 2025, students with vocational training are 35-50% more likely to secure jobs, showcasing the effectiveness of these programs.

Assessing Skills-Based Learning: Methods and Differences
In skills-based learning, assessments emphasize demonstrating skills rather than memorizing facts. Methods include projects, real-world tasks, portfolios, and continuous feedback, moving beyond traditional written tests. These assessments evaluate students' ability to adapt, solve problems, and apply skills in real-world scenarios, aligning with employer expectations.
Furthermore, they encourage ongoing learning by focusing on skill improvement over time. Instead of a final exam, students might complete a capstone project or internship to apply their skills in a real-world context, which is then evaluated by teachers and industry experts. Instructure emphasizes the importance of regular progress checks and feedback to support continuous growth.