Imagine setting goals that not only make sense but also fit perfectly with what your organization stands for. That's what a solid performance mapping framework can do. These days, businesses move fast, and getting a grip on these frameworks might just be your ticket to hitting those big targets. Studies show that companies using performance mapping are 30% more likely to hit their goals. In this guide, we'll walk you through the nuts and bolts of building a framework that works for you. Plus, we'll look at how adding outcome mapping can make your framework even better. Whether you're just starting out or tweaking what you already have, this article is full of insights and tips to help you tackle performance mapping with ease. Ready to dive into improving your strategic planning? Let's get started!
Understanding Performance Mapping Frameworks
Definition of a Performance Mapping Framework
A performance mapping framework is a strategic approach used to plan, monitor, and evaluate changes in behavior and performance within organizations or programs. Rather than proving direct cause and effect, this framework emphasizes how activities are linked to outcomes and their contribution to change.
A key aspect of this framework is the involvement of program implementers in selecting, collecting, and analyzing data. This participatory approach enhances their connection to, and utilization of, the findings. A notable example of this framework is Outcome Mapping, which focuses on behavioral changes and their contributions to outcomes instead of identifying precise causes.
Essential Elements of a Performance Mapping Framework
Setting Goals and Objectives
Defining clear goals and objectives is essential. This clarity serves as a guide throughout the mapping process, ensuring alignment and focus.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identify and map the essential skills, knowledge, and behaviors that are crucial for achieving role-specific or program outcomes.
Implementing Data Collection and Analysis
Implement participatory data collection and analysis. This approach ensures that stakeholders find the findings relevant and fosters a sense of ownership over the results.

Effective Reporting and Feedback
Utilize visual tools such as process maps or flowcharts. These tools are effective in illustrating workflows, identifying bottlenecks, and driving performance improvements.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Performance Mapping Framework
Define Purpose and Objectives for Performance Mapping
Purpose of Creating a Performance Mapping Framework
First things first, figure out why you need a performance mapping framework. What's the end goal? Is it to boost employee productivity, align personal goals with the company's big picture, or improve how you manage talent? Knowing exactly why you're doing this will guide every decision you make about the framework. Think about the current challenges your organization faces with performance management and how a well-structured framework can help tackle these issues. With a clear purpose, you can make sure the framework becomes a guiding light for your performance management efforts.
Key Outcomes for Performance Mapping Framework
Once you know why you're doing this, nail down the key outcomes you want from the performance mapping framework. Make them SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Maybe you want to boost employee engagement scores by 10% in a year or cut the turnover rate by 5% in six months. Clear outcomes give you something to aim for and a way to measure success. They also help you prioritize what to do and where to put your resources, ensuring the framework makes a real difference in managing performance.
Select KPIs and Metrics for Performance Mapping
Relevant KPIs for Employee Performance
Picking the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is key. They should reflect the organization's strategic goals and cover important aspects of employee performance like productivity, quality of work, teamwork, and innovation. Get input from managers and employees when selecting KPIs to make sure they're comprehensive and relevant. This team effort helps everyone buy into the framework, making sure it truly reflects the organization's priorities.
Measurable and Time-Bound KPIs
For KPIs to work, they need to be measurable and time-bound. This means setting clear criteria for measurement and specific timeframes to achieve them. If one KPI is to increase sales revenue, specify the percentage increase you expect and the timeline. This clarity helps track progress and spot areas needing improvement. Regularly reviewing and tweaking these KPIs keeps them aligned with changing business goals, ensuring they stay relevant and effective.
Designing the Performance Mapping Framework
Strategy and Objectives of the Framework
Designing the framework means coming up with a strategy that outlines the objectives, processes, and resources needed. This strategy should sync with the organization's broader goals and include a detailed plan for putting it into action. Look at the current state of performance management and pinpoint gaps the new framework will fill. A strategic approach ensures all framework parts work together toward the defined objectives.
Process for Setting and Reviewing Objectives
A crucial part of the framework is setting, cascading, and reviewing objectives. This involves creating a clear method for defining individual and team goals that align with organizational objectives. Cascading these goals helps everyone see how their work fits into the bigger picture. Regular reviews are vital to check progress, give feedback, and adjust as needed. This process keeps everyone accountable and focused on hitting the desired outcomes.
Cadence for Performance Measurement
Deciding how often to measure performance is another critical part of designing the framework. You need a balance between regular feedback and the practicalities of doing assessments. Monthly or quarterly reviews are common, but tailor the frequency to your organization's needs and resources. A consistent schedule makes performance measurement a regular part of the culture, not just a one-off task.
Consistent Performance Evaluation Scale
To evaluate performance consistently, create a clear rating or scoring scale. It should be easy to understand and apply across different roles and departments. Whether you use numbers, descriptive categories, or both, make sure the criteria for each level are well-defined and communicated. This consistency helps ensure fair evaluations and also helps spot trends and patterns in performance data.
Training and Development Programs
A solid performance mapping framework should include training and development programs. These should address skill gaps found in evaluations and support employees in hitting their goals. Offer a mix of formal training, on-the-job learning, and mentoring. By investing in employee development, you not only boost performance but also show you care about your workforce's growth and success.
Feedback Sessions and Check-ins
Regular feedback sessions or check-ins are crucial, allowing ongoing dialogue between employees and managers. These sessions should focus on progress towards goals, tackling challenges, and exploring improvement opportunities. Open, constructive communication fosters a culture of continuous improvement and strengthens team relationships. Scheduling these sessions regularly ensures feedback is timely and relevant.
Create a Visual Performance Map
Visual Tool for Employee Performance
A visual performance map is a handy tool that clearly shows employee performance and potential. Design it to present complex data simply and understandably. Use graphs, charts, or heat maps to show key metrics and trends. The visual map should quickly highlight high performers, areas needing improvement, and development opportunities. By making performance data visually engaging, you enhance understanding and drive better decision-making.
Customize Map with KPIs and Ratings
Customizing the visual performance map is crucial to ensure it reflects your organization's specific KPIs, goals, and performance ratings. Integrate the selected KPIs into the map and align them with organizational objectives. Include the rating or scoring scale for a comprehensive performance view. Customization ensures the map is relevant and tailored to your unique needs, boosting its effectiveness as a performance management tool.
Identify Strengths and Improvement Areas
The visual performance map should make it easy to spot strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. Use clear labels, color coding, and other visual cues to highlight key insights. The map should provide a holistic performance view, helping managers and employees quickly assess where they stand and what actions are needed. By making it easy to identify these elements, the map becomes a valuable resource for guiding performance discussions and development planning.
Implement Technology Solutions for Performance Mapping
Centralized Platform for Performance Data
Picking the right technology is crucial for making the performance mapping framework work. Choose a centralized platform or software that supports your framework’s goals. It should offer features like data integration, real-time analytics, and user-friendly interfaces. Look for options that are flexible and scalable to grow with your organization. A centralized platform keeps all performance data accessible and organized, making management and decision-making easier.
Integration with HR Systems
When choosing a technology solution, make sure it integrates with your existing HR systems. The platform should connect seamlessly with current HR tools and databases, ensuring smooth information flow. This integration reduces data silos and improves performance data accuracy and completeness. It also cuts down on administrative tasks, letting HR focus on strategic activities. Ensuring compatibility with existing systems maximizes the framework's benefits.
User Training for Effective Use
To get the most out of the technology, provide thorough training for all users. This includes employees, managers, and HR professionals using the platform. Training should cover its features, functionalities, and best practices. Offer ongoing support and resources, like user guides and help desks, to boost user confidence and competence. Well-trained users are more likely to embrace the technology and use it effectively to support performance management.
Roll Out the Performance Mapping Framework
Communicate Framework to Stakeholders
Communication is key when rolling out the new performance mapping framework. Inform all stakeholders—employees, managers, and executives—about the framework and its implications. Clearly explain the purpose, benefits, and how it will be used. Use various channels like meetings, emails, and intranet announcements to reach everyone. Transparent, consistent communication builds understanding and support for the framework.
Purpose and Benefits of the Framework
Besides communicating the framework, explain its purpose, benefits, and usage in detail. Highlight how it aligns with the organization’s goals and improves performance management processes. Emphasize benefits for both the organization and employees, like improved productivity, career development opportunities, and fair evaluations. Clear explanations address concerns and foster a positive perception of the framework.
Fixed Launch Date for Framework
Setting a fixed launch date is crucial for a smooth transition. Communicate this date well in advance to allow time for preparation and training. Consider holding a launch event or meeting to formally introduce the framework and celebrate its implementation. A well-planned launch ensures all stakeholders are aligned and ready to embrace the new performance management approach.
Ongoing Support and Feedback for Framework
Support System for Framework Users
For the framework to succeed long-term, set up a strong support system for users. Provide resources like user guides, FAQs, and help desks. Appoint dedicated support personnel or champions to assist users with questions or challenges. A solid support system ensures users have the help they need to use the framework and its tools effectively.
Continuous Feedback from Stakeholders
Ongoing feedback is vital for the framework’s success. Encourage employees, managers, and HR professionals to share feedback on its effectiveness and areas for improvement. Gather feedback through surveys, focus groups, or regular check-ins. Actively seeking and acting on feedback shows a commitment to continuous improvement, ensuring the framework stays relevant and effective.
Regular Framework Effectiveness Reviews
Regularly reviewing the framework’s effectiveness ensures it continues to meet organizational needs. Assess its impact on performance management processes and outcomes. Use metrics like engagement scores, turnover rates, and performance improvements to evaluate success. Based on these reviews, tweak the framework to enhance its effectiveness. Regular evaluation keeps the framework a valuable tool for driving performance and achieving goals.
Using the Performance Map for Decision-Making
Identify High Performers and Development Needs
The performance map is a valuable decision-making tool, providing visual data to identify high performers and those needing development. Use this info to tailor development programs, allocate resources, and make informed talent management decisions. Consider using the map to spot potential leaders or candidates for succession planning. By leveraging the map’s insights, organizations can make data-driven decisions that boost performance and drive success.
Support Talent Management and Rewards
The performance map plays a key role in supporting talent management, succession planning, and reward processes. By providing a clear view of performance and potential, it helps identify employees ready for promotion or needing more development. It also supports fair and transparent reward processes with objective performance data. Using the map in talent management ensures decisions are based on accurate, comprehensive info.
Ethical and Consistent Performance Reviews
To maintain the framework's integrity, ensure ethical and consistent application during performance reviews. Stick to established evaluation criteria and avoid biases or favoritism. Provide training for managers on conducting fair, objective reviews. Ensuring consistency and fairness builds trust in the performance management process and boosts employee satisfaction.
Step 1: Measurement Context for Performance Mapping
Start by defining the measurement context for your performance mapping framework. Understand the specific environment where performance will be measured, including organizational culture, industry standards, and external factors. Consider unique challenges and opportunities that might impact performance measurement and management. By clearly defining the measurement context, you can tailor the framework to meet specific needs and ensure its relevance and effectiveness.
Step 2: Develop KPIs and Metrics for Performance Mapping
Developing KPIs and metrics is crucial for the framework’s creation. Identify key indicators to measure performance and define metrics for each KPI. Consider a balanced scorecard approach for a comprehensive view of performance across dimensions like financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. Clear, measurable KPIs and metrics ensure accurate performance assessment and management.
Step 3: Technical Setup and Data Collection for Framework
The technical setup and data collection process supports the performance mapping framework. Select and configure tech solutions to collect, store, and analyze performance data. Use automated data collection tools for accuracy and efficiency. Ensure consistent, secure data collection to maintain integrity. A robust technical setup and data collection provide a strong foundation for effective performance management.
Step 4: Organize and Prioritize KPIs
Organizing and hierarchizing KPIs ensures performance data is meaningful and actionable. Categorize KPIs based on their importance and relevance to organizational goals. Use a hierarchical structure aligning KPIs with strategic objectives, departmental goals, and individual performance targets. Clear organization helps prioritize initiatives and focus on critical improvement areas.
Step 5: Performance Monitoring and Evaluation
Implement performance monitoring and evaluation by establishing processes to track and assess performance against KPIs and metrics. Use dashboards and reports for real-time insights into performance trends and progress. Regular monitoring and evaluation quickly identify and address performance issues. Effective monitoring and evaluation drive continuous improvement and help achieve performance objectives.
Step 6: Continuous Improvement for Performance Mapping
Continuous improvement and adjustment ensure the framework’s long-term success. Regularly review the framework’s effectiveness and make adjustments to enhance its impact. Use feedback from stakeholders and performance data to spot improvement areas. A culture of continuous improvement ensures the framework remains relevant and effective in supporting performance management and achieving goals.
For more insights on performance mapping, visit HiBob's blog on performance mapping. Additionally, BSC Designer offers resources on performance measurement and mapping techniques.
Integrating Outcome Mapping with Performance Mapping Framework
Outcome Mapping: A Key Component
Outcome Mapping focuses on how people change—whether they're individuals, groups, or organizations involved in a project. It's a people-first, learning-focused method that views projects as social efforts requiring collective participation for success.
Key Steps:
- Identify Boundary Partners: Determine who your boundary partners are—these are the individuals or groups you directly interact with and aim to influence.
- Set Progress Markers: Establish markers to track progress and keep tabs on outcomes with journals.
This approach prioritizes learning and improvement over strict adherence to rules, often utilizing self-assessment and reporting. It's flexible enough to integrate with other methods like logical frameworks and Results-Based Management, providing a comprehensive picture that combines behavior changes with results-focused metrics.

Integrating Outcome Mapping into Performance Frameworks
-
Define Your Project Vision: Begin by setting a clear project vision and understanding the context and key players involved.
-
Identify Boundary Partners: Find the people or groups you interact with directly and aim to influence.
-
Set Outcome Challenges and Progress Markers: Keep an eye on gradual changes by setting outcome challenges and progress markers.
-
Create Strategy Maps: Develop strategy maps to illustrate how project activities lead to the desired behavior changes.
-
Blend with Performance Mapping Frameworks: Combine performance mapping frameworks with behavioral insights and performance metrics for a comprehensive view.
-
Implement Cycles of Monitoring and Reflection: Use cycles of monitoring, reflection, and tweaking to continuously improve.
-
Utilize Visualization Tools: Employ visualization tools and value stream mapping techniques to track progress and maintain clarity.
By following these steps, you can effectively integrate Outcome Mapping into your projects, ensuring a balanced approach that values both behavioral changes and performance outcomes.

FAQ
Integrating Outcome Mapping into Performance Management Frameworks
You can blend Outcome Mapping with current frameworks by honing in on its central idea: changing behaviors in people, groups, and organizations that a program touches. This complements traditional frameworks that focus more on measuring outputs and outcomes.
Outcome Mapping is particularly effective for dealing with complex, non-linear changes, making it a good fit for adaptive and participatory monitoring and evaluation setups. It actively involves program implementers in choosing, gathering, and analyzing data. This involvement helps them take ownership of the findings and boosts participation.

For instance, you could merge Outcome Mapping with a Balanced Scorecard by adding indicators of behavioral change and processes for participatory monitoring to capture contributions to complex changes more effectively.
Unique Features of Outcome Mapping in Performance Frameworks
Outcome Mapping zeroes in on behavioral shifts in stakeholders rather than just outputs or direct cause-and-effect, unlike linear change models. It manages non-linear change processes and calls for program implementers' participation, which is different from top-down or data-driven methods.
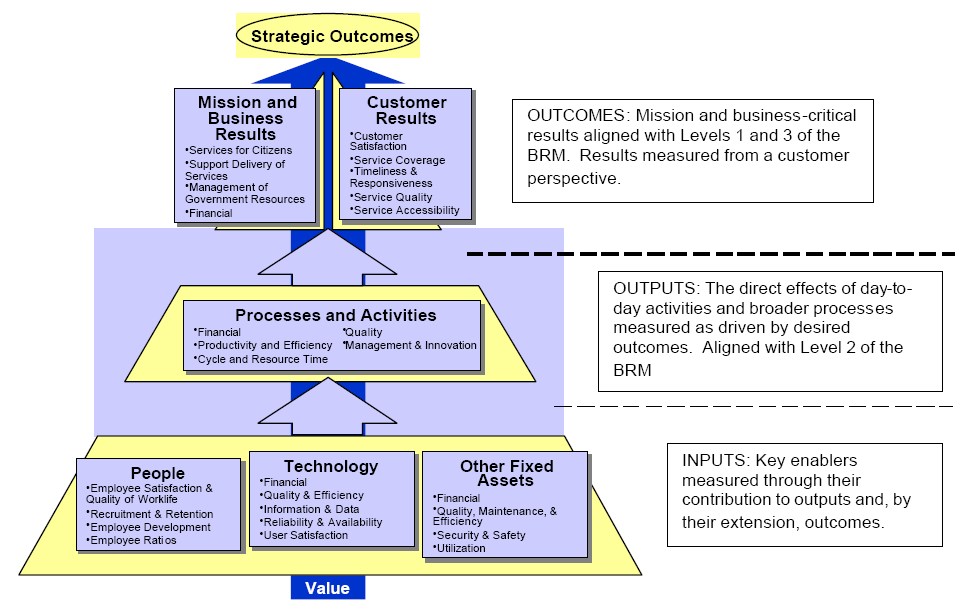
While frameworks like the Balanced Scorecard focus on set indicators or KPIs, Outcome Mapping connects activities to behavioral changes without trying to prove direct causality.
Challenges in Implementing Outcome Mapping Frameworks
Using Outcome Mapping comes with challenges. It requires active participation from program implementers in data collection and analysis, which takes extra time and capacity building.
Its non-linear nature can be tough to fit into rigid systems, and showing impact to stakeholders used to traditional frameworks can be tricky. Organizations might find it hard to adapt their current practices to the flexible, participatory approach that Outcome Mapping requires, which means staff training is necessary to shift from output-focused to behavior-focused monitoring.